Trading technical indicators with binary options can be a highly profitable trading style – if you know how to do it right. Our article explains the basics and three examples of strategies you can use. Specifically, you will learn:
- What are technical indicators?
- Why are technical indicators and digital options a great combination?
- Three examples of strategies for technical indicators
With this information, you will immediately be able to trade binary options with technical indicators.
What are metrics?
Technical indicators are useful trading tools that allow price action traders to understand what is happening in the market and make predictions about what will happen next.
Some indicators pull their results directly into price charts, making it easy for analysts to compare them to current market prices. Other indicators use a separate window to display their results. The most famous example of this type of indicator is the oscillator. These indicators generate a value that fluctuates between 0 and 100. This value and its change over time allows you to understand what has happened in the past and what will happen next. .
There are thousands of indicators, but here are the most important ones and a few examples:
- Support & resistance: These indicators predict support and resistance levels to which the market is likely to turn. When it breaks through such a level, it will likely create a strong move away from the price level. Example: Bottom, Fibonacci Retracement, Pivot Point (PP), Top.
- Trends: These indicators help you gauge the strength and reliability of the trend. Examples: Average Directional Index (ADX), Commodity Channel Index (CCI), Bearish Price Oscillator (DPO), Certainty Oscillator (KST), Ichimoku Kinkō Hyō, Moving Convergence/ moving average divergence (MACD), Moving Average Mass Index (MA), Parabolic SAR (SAR), Smart Money Index (SMI), Trix Vortex Indicator (VI).
- Momentum: These indicators help you understand the momentum of a movement. Examples: Money Flow Index (MFI), Relative Strength Index (RSI), Random Oscillator, True Strength Index (TSI), Williams Ultimate Oscillator %R (%R).
- Volume: These indicators use trading volume (the number of assets sold or bought) to gauge whether investors are bullish or bearish. Examples: Accumulation/Distribution Current, Ease of Movement (EMV), Force Index (FI), Negative Volume Index (NVI), Balanced Volume (OBV), Put/Call Ratio (PCR) , Volume Price Trend (VPT) .
- Volatilization Indicators: These indicators measure the strength of a movement, helping traders to make a variety of predictions, especially for binary options types that use target prices, for example. e.g. one touch option, boundary option or ladder option. Examples: Average True Range (ATR), Bollinger Bands (BB), Donchian channel, Keltner channel, CBOE, Market Volatility Index (VIX), Standard Deviation ().
There is no need to learn all of these indicators. Take a look at each, pick the one you like best and take it from there. It is best to start with an indicator that you really understand and like. You can then add more indicators to your strategy, allowing your trading to grow naturally.
Why are indicators suitable for binary options?
Most binary options traders rely heavily on technical indicators. There are three main reasons for this strong connection between binary options and technical indicators:
- Technical indicators simplify price action analysis. Price action is the only way to predict what will happen on such short timeframes when you use in binary options. Just looking at price movements can be confusing, though. Technical indicators can filter the most important information of the price chart and display it in a way that everyone can understand immediately. This simplification makes your transactions faster and easier.
- Indicators that guarantee your trading. When you analyze the market without any help, there is a lot of information that needs to be entered. Complexity leads to mistakes and bad decisions, both of which cost you money. Technical indicators eliminate these mistakes, that’s why they make you more money simply – a great combination.
- Indicators can reveal things not traders can. In a snap, technical indicators analyze hundreds of data sets, filter out the most relevant information and display it in a way that everyone can understand. Without the help of technical indicators, most of this information would not be accessible. It would take years to calculate the bollinger bands for fifty assets with ten time periods each. Technical analysis adds layers of information to your trading that will be hidden.
These points are why technical indicators and binary options are such a great combination.
What are the leading indicators?
Leading indicators are a special form of market indicators. Market indicators are everything that helps you understand whether the price of an asset will rise or fall in the future. They provide an important, useful and easy to understand tool for binary options traders. With the right strategy, they can help you predict new market movements and find the perfect time to invest.
These indicators can be classified into two categories:
- Top Index. This type of indicator predicts what will happen to the price of an asset.
- The index lags. This type of indicator tells you what happened to the price of an asset. While this information is supposed to help you predict what will happen next, the indicator itself focuses on the past – this is the big difference between both types of indicators.
The goal of leading indicators is to give you a sense of where an asset’s price is headed. A great example of a leading indicator from another sector is the business climate index. Business managers report their expectations for the future, and the index creates an aggregate value that can be easily compared with previous months and years. Its value and changes over time help you predict whether the economy will improve or get worse.
The leading financial indicators do the same thing. They measure something, and the resulting value tells you whether things will get better or worse.
Why should I use leading indicators?
Leading indicators serve a very important purpose: they can help you understand whether an existing movement is more likely to continue or end prematurely. With this sign, you can find great trading opportunities and avoid the bad ones.
For example, suppose that you find an upward movement.
- If your leading indicator tells you that the movement is likely to continue, you know that this is the right time to trade a high.
- If your leading indicator tells you that the movement is likely to end soon, you know that now no should be the right time to trade a high option. You should stay out of the market or trade an option that predicts the end of the movement.
For any trend follower, swing trader and almost everyone else, leading indicators add important information to their trading style. They can help filter out bad signals, find new trading opportunities and win more trades.
Popular examples of leading indicators
There are hundreds of leading indicators. Some of them are similar, some are very different. To help you better understand the leading indicators, we will now look at three different examples of leading indicators that will give you a good feel for the different types of leading indicators.
Example 1: Cash Flow Index (MFI)
The Money Flow Index (MFI) is such a popular leading indicator because it helps traders quickly gauge the strength of a trend.
As the name suggests, MFI compares money flowing into an asset with money flowing out of it. For this purpose, it multiplies the average of the high, low, and closing prices of each period by the period’s volume and then divides the sum of all periods by the rise in prices by the sum of all periods by reduced price.
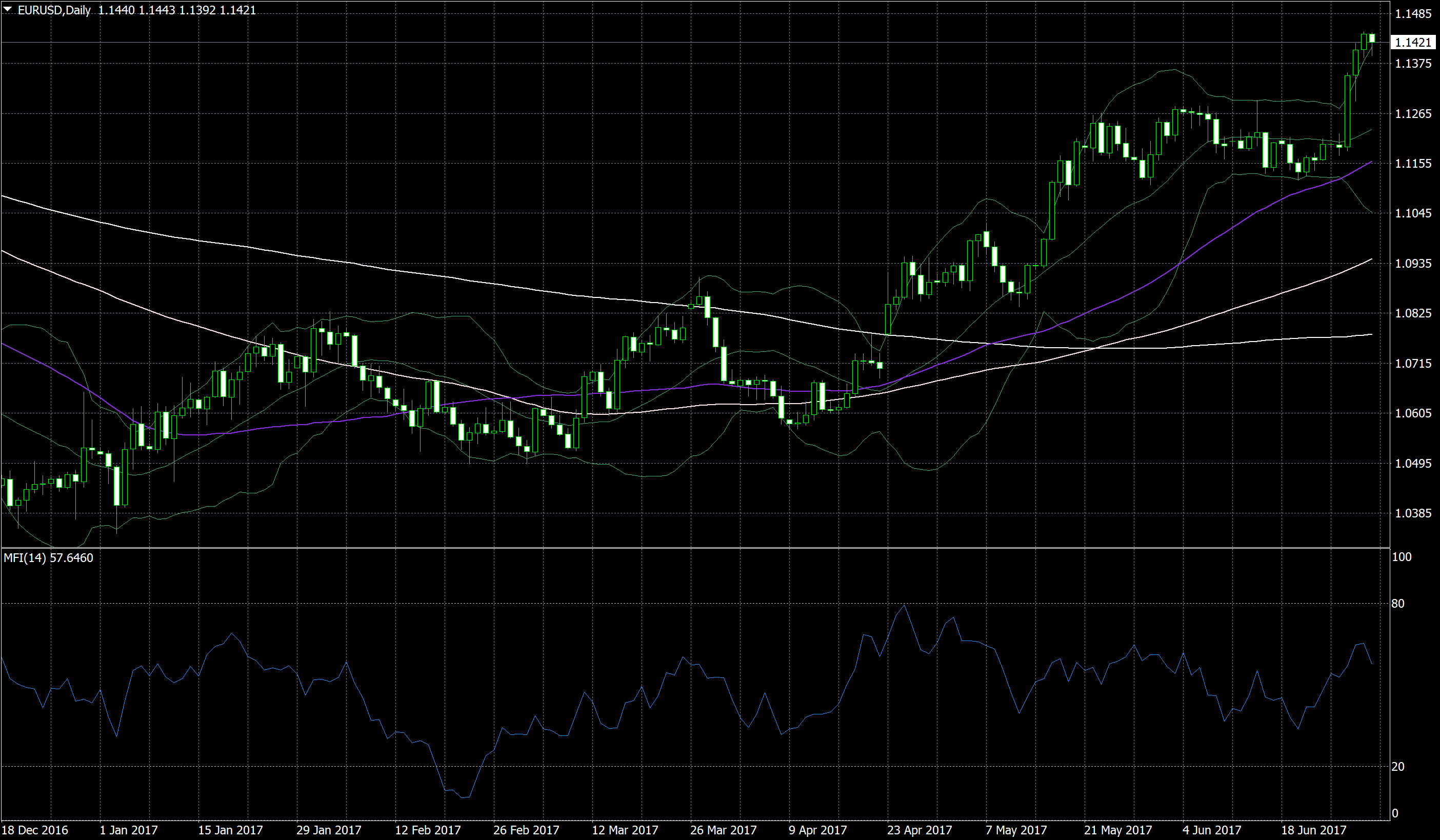
The result is a value between 0 and 100.
- When the MFI reads 100, all the money flows into one asset – all periods have a bull phase.
- When the MFI reads 0, all money has flowed out of an asset – all periods are bearish.
- When the MFI reads 50, the number of assets sold and bought is exactly the same.
Every value above 50 indicates that more sellers are buying the asset, any value below 50 indicates the opposite.
The reading of the MFI and the change of the MFI over time allows for two predictions about future market movements:
- Extreme value. When the MFI is too high (usually above 70) or too low (usually below 30), the market enters extreme areas. Traders claim that such extreme values indicate that too many traders have bought or sold an asset and no more traders can buy or sell that asset and keep moving. Therefore, they predict that the movement is in trouble and will soon turn around or undergo a consolidation before it can resume. Some traders use this signal to stop investing in the movement; some have invested in the opposite direction.
- Convergence / Divergence. When the market forms a new extreme in a trend (a new high in an uptrend or a new low in a downtrend), the MFI should also reflect this movement and create an extreme as well. new. When the MFI doesn’t reflect the market’s new high/low with its own high/low, traders have stopped driving the trend. While this should still be enough to create a new extreme, a sustained decline will end the trade. Some traders will use this signal to stop investing in a trend, some to invest in the opposite direction.
Of course, you can also interpret the MFI the other way around:
- When the MFI reads between 30 and 70, there is enough room for the market to continue its current movement. Most traders would predict that the movement will continue for a while and invest accordingly.
- When the MFI reflects the current trend, the trend remains intact. Most traders will predict that the trend will continue and invest accordingly.
The MFI is a leading indicator because it predicts that a trend or movement will continue or end soon. Lagging indicators will only tell you what happened to a movement in the past.
Since the value of the MFI fluctuates between 0 and 100, it is called an oscillator. Most other oscillators are leading indicators, too. If you like the simple idea of basing your investment decisions, check out the other oscillator technical analysis has to offer.
Example 2: Commodity Channel Index (CCI)
Don’t let the name fool you – The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) works with all asset classes, not just commodities.
Simply put, CCI calculates how far an asset has diverged from its statistical significance. The theory is that when an asset strays too far from its average price, it will soon have to turn around. Just like with the MFI, the CCI assumes that when too many traders have bought or sold an asset, there is no one left to push the market further in this direction. It has to come back and solidify.
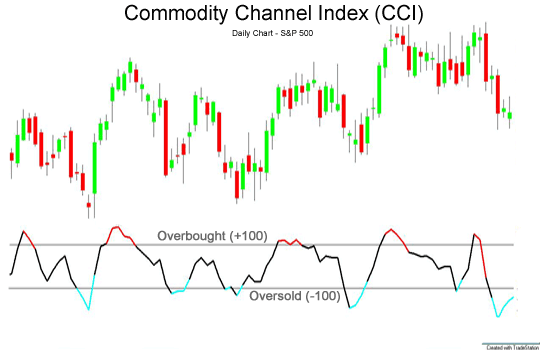
Specifically, CCI multiplies the average price of the highest, low, and close times by 0.015 and sets the result relative to a smooth moving average.
- A value above 100 indicates that the asset is trading 1,015 times the moving average value.
- A value below 100 indicates that the asset is trading 0.985 times the moving average value.
In both cases, CCI predicts that the market has moved too far from the moving averages and that the movement will soon turn around.
Some traders also wait before they invest.
- Once the CCI has gone up over 100, they wait until it starts to fall before they invest.
- Once the CCI has dropped below -100, they wait until it starts to rise before they invest.
Traders use CCI more as a lagging indicator. To use CCI as a leading indicator, you have to invest when the market crosses the +100/-100 lines – then you invest in the prediction. When you trade in the direction of the change, you invest in the reaction and use the CCI as a lagging indicator.
Sometimes the line between lag and lead can be thin. As long as you know the difference and trade accordingly, you should be fine.
Example 3: Relative Strength Index (RSI)
At first glance, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) looks quite similar to the Money Flow Index (MFI). Both are oscillators, generating a value between 0 and 100 and using overbought and oversold zones.
The difference between both indicators is that the RSI only focuses on price changes while the MFI also looks at the volume of each period. While the RSI treats all time periods equally, the MFI places more weight on high volume periods and less weight on low volume periods.
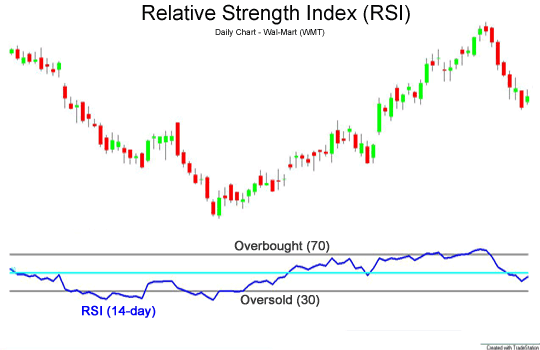
Alternatively, you can use the RSI just like the MFI. Trade divergence and oversold areas above 70 or below 30. When the RSI is between 30 and 70, the current movement still has some room; When it reflects a trend, the trend is good.
Both MFI and RSI are always better. Which indicator you should use depends on your strategy, personality and beliefs about the market.
- Some traders argue that they trade price, not volume and therefore, they should ignore volume. They also say that the volume is too similar on the short timeframes of binary options to have any effect. Traders should use the RSI.
- Some traders argue that volume has a significant effect because it tells you which direction more traders support. Traders should use MFI.
How to trade top indices with binary
All the leading indicators can be the sole basis of your trading strategy or an additional feature to your existing strategy for signal filtering. We will cover strategies using leading indicators both ways.
Strategy 1: Trade MFI Divergence with high/low options
We have shown that the MFI reflects an intact trend.
- When an intact uptrend makes a new high, the MFI also makes a new high.
- When an intact downtrend makes a new low, the MFI also makes a new low.
When the MFI does not reflect the new extremes of the trend, the trend is in trouble. The trend is losing momentum, and while it still has enough strength to make new extremes, it looks like this is the last extreme of the trend.
High/Low Options give you the perfect tool to trade this prediction.
- When the MFI diverges in an uptrend, invest in a low option.
- When the MFI diverges in a downtrend, invest in a high option.
The important part of this strategy is the expiration date. While it is highly likely that the market will follow the MFI divergence by changing direction or entering a sideways movement, these movements take time to develop. It is important that you choose your shelf life long enough to give the market this time.
For example, when you find MFI divergence in the 5-minute chart, the 15-minute expiry will not be enough. The market will take at least 10 periods to rotate, and a 15 minute expiration will only equate to 3 bars. Choose a expiry of one hour and you will increase your chances of winning the trade.
You can also trade this strategy with the RSI indicator. You will only convert the indices, without changing anything else.
Alternatively, you can replace high/low options with low-risk ladder options. Ladder options work like high/low options but allow you to use prices other than the current market price as a reference point for your prediction.
- After an MFI divergence in an uptrend, you predict that the market will trade one price lower than the current market price.
- After MFI divergence in a downtrend, you predict that the market will trade one price below the current market price.
This is the safer version of the strategy. Instead of using the current market price as a reference point for your prediction, you use the price that lies further down the direction in which you expect the market to go away. This strategy will give you a higher percentage of trades but also get you a lower payout percentage. Decide for yourself which strategies you want to use.
Strategy 2: Filter Trends with RSI
A trend following strategy follows a simple principle:
- In an uptrend, invest in rising prices.
- In a downtrend, invest in falling prices.
Despite this simplicity, many traders fear that they might invest in a trend that will end soon. Traders can use the RSI to filter signals.
- Once the RSI has doubled in trend, invest in the trend.
- Once the RSI has diverged from the trend, do not invest in the trend.
Adding the RSI to a trend following strategy can help traders gain a higher percentage of their trade and make more money with a simple check.
Keep the rest of your strategy unchanged. Use expiration as before and invest the same percentage of your overall account balance on each trade.
Strategy 3: Trade MFI extremes with high/low options
In addition to divergences, the MFI also creates a prediction when a movement enters an extreme area. This prediction allows for a simple trading strategy:
- When the MFI enters the overbought zone, invest in a low option.
- When the MFI enters the oversold area, invest in a low option.
The success of this strategy depends on your ability to pick the right deadlines. The market will take a while to turn around, that’s why you must avoid choosing too short a term. When you choose an expiry that is too long, on the other hand, the movement may end by the time your option expires.
Experience will help you find the right deadline. The perfect setting depends on the situation, your charting period and the characteristics of the asset. If you’re looking for a rough number to start with, try about 5 periods, and then take it from there.
Similar to the first strategy, you can also trade this strategy based on the RSI or with low risk ladder options.
Top Indicators – Summary
Leading indicators are an important, useful and easy to understand tool for market analysis. Binary options traders can use leading indicators as the sole basis of their strategy or to filter signals. They are especially useful for finding the right timing and avoiding bad trading opportunities.
What are the latency metrics?
Lagging indicators are an important aspect of any market analysis strategy. This article explains everything you need to know to trade binary options based on lagging indicators. You will also understand their advantages, disadvantages and ideal areas of use.
The difference between leading and lagging trading indicators is the same.
- Lagging trading indicators tell you what happened to an asset’s price in the past in a way that helps you predict what will happen next.
- Top indicators analyze another factor and predict how it will affect the price of an asset.
This difference is why lagging indicators are especially useful during trending periods. When the market is in a trend, lagging indicators can help you make great predictions; but when the market is not trending, many lagging indicators use their predictive qualities.
Lagging indicators serve an important purpose and are an important part of any market analysis strategy. To see how you can use lagging indicators for your trading, let’s take a closer look at three common examples of lagging indicators.
Common examples of lag metrics
There are hundreds of lagging stats, but let’s keep things simple. Here are the three most common lagging indicators that every trader should know.
Example 1: Trend
The most common example of a lagging indicator is the trend. Trends are zigzag movements that take the market to new highs.
Trends are zigzag movements because the market never moves in a straight line. Every once in a while, every movement has to take a break to build new momentum. It is simply not possible for all persistent traders to continue buying.
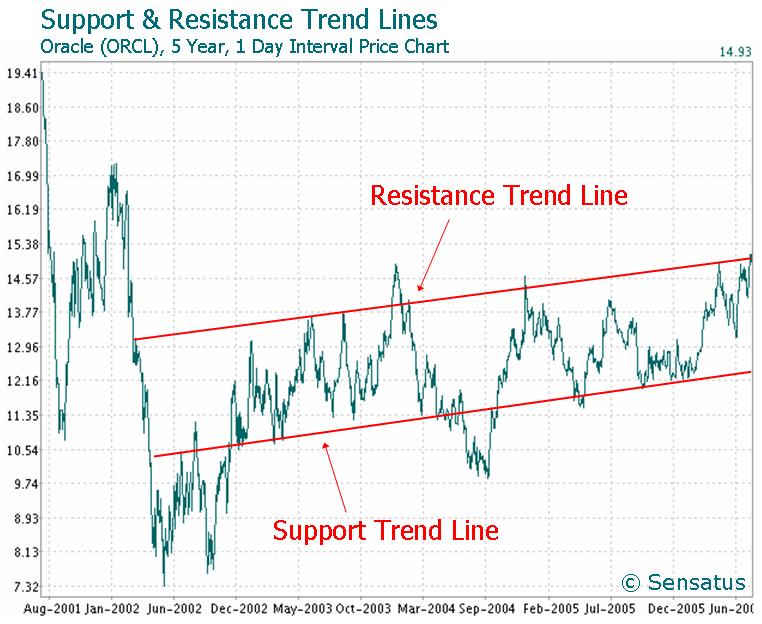
This is why trends go two steps forward and one step back. The resulting zig-zag movements are easy to identify and allow for accurate predictions.
- Uptrends consistently make higher highs and lower lows.
- Continually downtrend makes lower lows and lower highs.
A trend strategy predicts that the current trend is likely to continue.
- When the market is in an uptrend, trend traders invest in the uptrend.
- When the market is in a downtrend, trend traders invest in falling prices.
Some traders also trade every swing in a trend. The swing is a movement from high to low and by trading multiple swings in a trend swing traders hope to increase their profits.
Of course, no trend will continue indefinitely. But even with high/low options, you will only need to win 60 percent of your trade to make money. A well-executed trending strategy can easily achieve this goal.
The trend is a lagging indicator because it tells you that the market has trended over the past periods. While this knowledge also allows for predictions about what will happen next, the main indication of a trend is based on past price movements.
Trend is also the most important lagging indicator. Most other lagging indicators lose predictability when the market is not trending, which is why trend analysis should precede the use of other technical indicators.
Example 2: Moving Average
Another common example of a lagging indicator is a moving average. The moving average will calculate the average price of the previous periods and draw it to your chart. Then it repeats the process for all previous stages and connects the dots with a line.
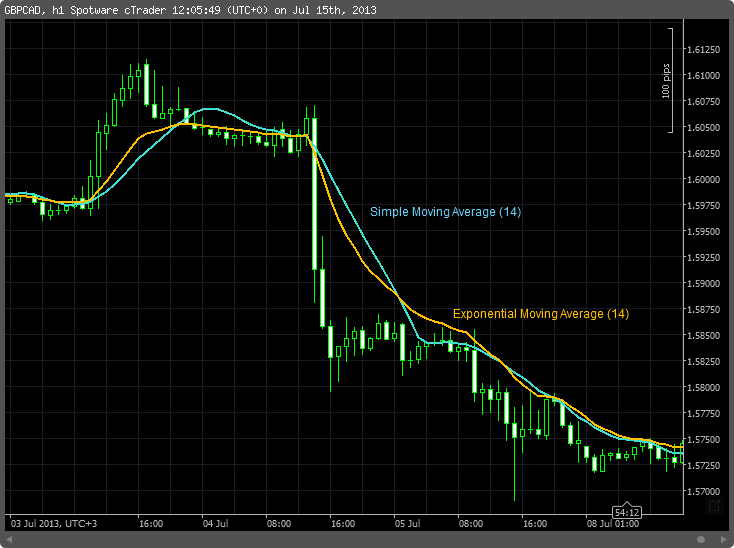
The position and direction of the moving average can tell you a lot about an asset’s price did:
- When a moving average moves up, the market must rally in the late stages. When it turns downward, the market must fall.
- When the market trades above the average, the market must rise in the late stages. When the market trades below the average, the market must fall.
When both of these directions are in the same direction, you get a good indication of what’s going on.
- When the market is trading above the and moving averages are pointing upwards, the market is likely to rise.
- When the market is trading below the and moving averages are pointing downwards, the market is likely to fall.
These guidelines help you make better investment decisions.
Example 3: Bollinger Bands
Bollinger bands are a popular indicator because they create a price channel in which the market is likely to remain. This price channel consists of three lines or bands:
- 20 period moving average is the middle line.
- One line above twice the standard deviation above midline.
- One line less than twice the standard deviation below the midline.
The market always never leaves the two lines outside of the Bollinger Bands. The midline acts as a weaker resistance or support level, depending on whether the market is currently above or below it.
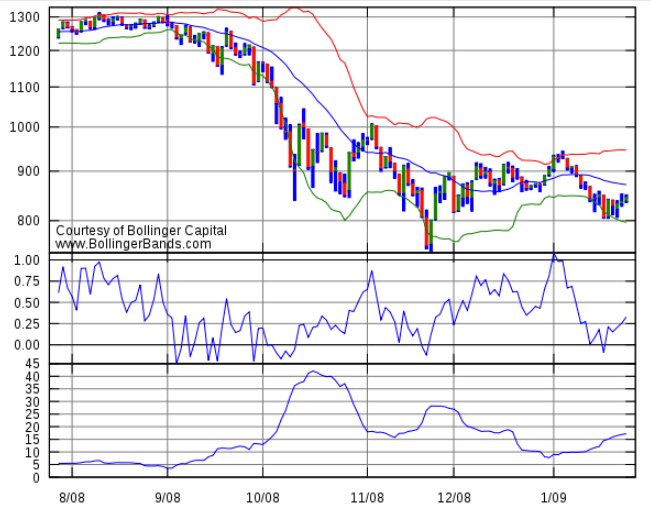
Bollinger bands can help you understand whether an asset’s price is likely to rise or fall.
- When an asset is trading near the upper range of the Bollinger Bands, it leaves no room to climb further. Therefore, it is likely to decrease.
- When an asset is trading near the lower range of the Bollinger Bands, it leaves no room to fall further. Therefore, it is likely to increase.
- When an asset is approaching the mid lane, it is likely to take a break. Sometimes, the market will cross the midline; sometimes it will come back
These instructions provide you with many trading opportunities.
Bollinger bands are lagging indicators because they only tell you what happened in the past. Moving averages and standard deviations are both based on the last 20 periods. While it is likely that the market will also adhere to similar sentiments for the time being, Bollinger Bands cannot predict a trading range 50 periods from now. After that, the market environment will change, and the trading range will be different.
Despite this limitation, Bollinger Bands can be a valuable part of your trading strategy. We will see later.
Why should I use latency metrics?
Some binary options newbies question whether lagging indicators can help them. They point out that any trader has to predict what will happen next and argue that indicators telling you what happened are of little help with this task.
Traders are confused. Lagging indicators can provide valuable predictions and help you gain market insights. There are two main reasons why traders use lagging indicators:
- Latency metrics are based on proven facts; leading index is nil.
- Understanding what happened helps you predict what will happen next.
Let’s take a closer look at the three advantages of lagging indicators.
Advantage 1: Latency metrics are based on proven facts, leading metrics are not
When the 50-period moving average is pointing upwards, you know that the price of an asset has increased more than it has declined over the past 50 periods. This result is indisputable. Similarly, when the market is currently trading below the moving average, you know that the market has picked up some bearish momentum recently.
This knowledge puts your trading strategy on solid feet. Conservative traders in particular will prefer lagging indicators as they provide them with a certain base from which they can make their decisions.
The leading indicators are different. Volume is a leading indicator, for example. The volume strategy predicts that a decrease in volume signifies the impending end of a movement. This may be true, but it is uncertain, and the connection cannot be proven – you have to believe it. While volume is slowing down, the price movement may even accelerate. Sometimes, a decrease in volume indicates an ending movement; sometimes not.
Simply put, lagging indicators focus on known past price movements. Leading indicators imply that another factor will influence future price movements – you may believe there is a connection, and there may be, but there are many other factors influencing the market, that is why it is impossible to say whether this connector will affect the market at all and whether it will affect the market more strongly than other connectors.
Advantage 2: Understanding what happened helps you predict what will happen next.
Lagging indicators also allow predictions of what will happen next – they just do it indirectly.
Leading indicators imply that a certain factor will determine where the market will go next. The latency index makes no such assumption. They are simply predicting that what happened before will continue.
When the market crosses a moving average, lagging indicators only tell you what happened – the market has recently changed direction. The implied assumption is that this movement will continue.
- If the market is falling in the recent past, it seems likely that the same factors that have pushed the market down in the recent past will also push it down in the short term.
- If the market is bullish in the recent past, it seems likely that the same factors that have pushed the market in the recent past will also push it up in the short term.
Both predictions are tradable.
In general, binary options trading requires you to understand what is happening right now. Since there are so many factors at work right now, it’s impossible to tell which is happening with absolute certainty. But understanding what happened is an essential part of coming up with a tradable prediction that will be correct under enough circumstances for you to make money.
How to trade lagging indices
Let’s get concrete. Here are three strategies on how you can trade lagging indicators with binary options.
Strategy 1: Trade trend changes with one-touch options
Each trend consists of many oscillators. Every single swing provides a great trading opportunity for one-touch options as it incorporates powerful indications of the direction and length of the movement.
Every movement in the main trend direction is followed by a movement in the opposite direction and vice versa. This simple relationship makes predicting the direction of the market simple once you spot a swing.
Now you can simply trade this signal with high/low options, but the oscillator also allows you to trade one-touch options, which offers much higher payouts but requires you to predict the length of the motion.
In a trend, the oscillator in the main direction will always move at least to the extreme extreme.
- In an uptrend, the next increase in price will reach at least the price of the previous high.
- In a downtrend, subsequent downward movements should reach at least the price of the previous low.
The change in the direction of the main trend follows the same clear rules. The market usually reverses a third or two-thirds of the previous movement in the direction of the main trend.
- In an uptrend, a downward slide reverses about one-third to two-thirds of the previous upward swing.
- In a downtrend, an upward slide reverses about one-third to two-thirds of previous downward movements.
With this knowledge, you achieve the clear price target you need to trade one-touch options. Here’s what you do:
- Waiting for a swing to finish.
- Determines the reach and direction of the next swing.
- Check if your broker offers you a one-touch option with a target price within reach of this movement and actual expiration. If so, trade it. Otherwise trade options high/low in the direction of the move.
At this point, it is important to mention that movements against the main direction of the trend are usually more volatile and take longer to develop. Many traders avoid reverse trading with one-touch options and use high/low options instead. Decide for yourself how you want to trade the reversal.
Strategy 2: Trade the market crossing the moving average with high/low options
When the market crosses a moving average, it has clearly changed direction. You can predict that this new movement will continue and invest in a high/low option in the direction of the movement.
- When the market crosses your moving average below, invest in a low option.
- When the market crosses your moving average upwards, invest in a high option.
The important aspect of this strategy is that you choose the right expiry date. For example, a 9-period moving average can never predict what will happen to an asset’s price over the next 50 periods. 50 periods and 9 periods are simply too different time frames.
To avoid making predictions that cannot be made based on your moving average, always keep the expiration time shorter than the time that is the basis of your moving average. Ideally, you would use an expiry that is less than half of your moving average.
Similarly, you should avoid using too short a term or short term market volatility that could cause you to lose a trade despite making an accurate prediction. Using expiry at least a quarter of the time is the basis of your moving average.
For example, when you use a moving average based on 20 periods and a price chart with a duration of 5 minutes, your moving average is based on 100 minutes (20 times 5). Ideally, you would trade this moving average with a shelf life of 25 to 50 minutes. You could also go a little longer or shorter, but the 60 second expiry would be too short and the 4 hour one would be too long.
Strategy 3: Trade Bands with Low Risk Ladder Options
Bollinger bands represent the trading range of the market and ladder options allow you to predict which prices are out of reach of the market – this is a great combination.
The success of this strategy also depends on choosing the right deadline. Bollinger bands are lagging indicators which is why they cannot predict what will happen in ten periods on the way. By then, the market will change and the sign of the Bollinger Bands will change accordingly.
To ensure that the Bollinger Bands in your chart make a valid prediction for your option, you must set the period of your chart to the same value at expiration or so. The important point is that your option expires during this period because Bollinger Bands only generate predictions for this period.
When you think about trading an option with an expiry of 15 minutes, you need to use at least a 15-minute chart. If ten minutes have passed in the current period, you must switch to the 30-minute chart to ensure that your option expires in the current period.
All you have to do to implement this strategy is:
- Set your char interval by expiry.
- Analyze the upper and lower price ranges of your Bollinger Bands.
- Find a ladder option with a target price outside these boundaries.
- It is predicted that the market will not be able to reach this price.
For example, let’s say that an asset is trading for £100. The upper Bollinger band is at £101 and the lower band is at £99.5. Your expiry and chart time is 30 minutes and no time has elapsed in the current period.
- If your broker offers a ladder option with a target price of £101.5, you will know that the target price is outside the range of the Bollinger Bands. Therefore, you should invest in a low option based on this target price, thereby predicting that the market will not be able to reach this price.
- If your broker offers a ladder option with a target price of £100.5, you will know that the target price is within reach of the Bollinger Bands. This target price would be a bad investment based on this strategy.
With this strategy, you will get relatively low payouts. Since you will be able to win the overwhelming majority of your trades, you can make a profit anyway.
Summary
Lagging indicators are an important aspect of any market analysis strategy. They give definite indications of what happened and allow for a qualitative prediction of what will happen next. Strategies based on trends, moving averages and bollinger bands have helped many traders create successful trading strategies.
Three examples of strategies for technical indicators
To get you started with binary options and technical indicators, here are three examples of strategies you can use.
One: Trading MFI/RSI Extremes
Money Flow Index (MFI) and relative strength index (RSI) are simple to interpret technical indicators based on similar ideas. Both indicators are oscillators and both calculate the magnitude of a movement by relating its current momentum to past momentum. The difference is that the MFI also looks at volume while the RSI alone focuses on price action. Choose the metric you prefer; it will make little difference to your final strategy.
Both MFI and RSI identify overbought and oversold zones.
- When traders have been buying an asset for too long, the MFI and RSI think that there are not enough buyers left in the market to continue pushing the price up. The market is overbought and likely to turn around.
- When traders have been selling an asset for too long, the MFI and RSI think that there are not enough sellers left in the market to continue pushing the price down. The market is oversold and is likely to turn around.
Based on this simple prediction, you can trade binary options. When your index of choice reaches an extreme value, invest in the opposite direction and predict that the market will soon turn around. Some traders also invest when the market leaves an extreme area, arguing that it is better to invest in a reversal that has already occurred (as indicated by the market leaving the extreme area) than is an impending turnaround (as indicated by the market going into regional extremes). Some traders also wait a few periods before they invest and see if the market is in an extreme zone.
Two: Bollinger Bands Trading
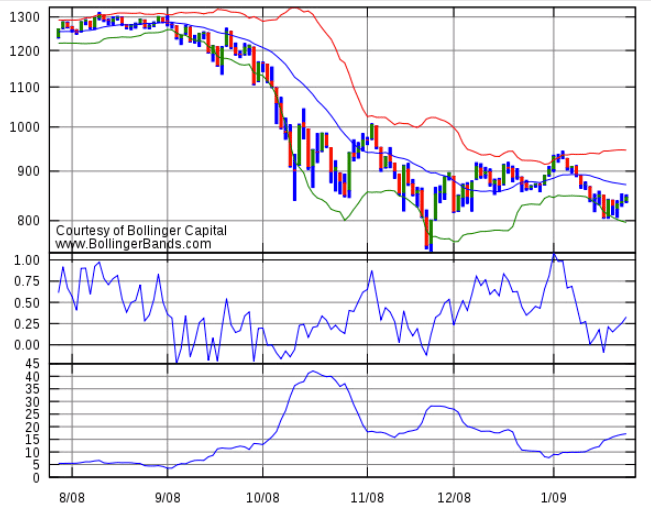
Bollinger bands are a great technical indicator for binary options traders as they clearly indicate the price level at which you should expect price action.
Bollinger Bands create a price channel consisting of three lines. People who have:
- A moving average . The middle line of the Bollinger band is a moving average, usually based on 20 periods.
- One line above . By adding twice the standard deviation to the moving average, the bollinger bands create the upper line.
- One line lower than . By subtracting twice the standard deviation from the moving average, the bollinger bands create a lower line.
The result of this process is a price channel that surrounds the current market price. Each line acts as a resistance or support level, depending on which direction the market approaches the line.
- When price approaches a line from the top, it acts as an support .
- When price approaches a line from below, it acts as an resistance .
Traders can trade these lines in two ways:
- A revolving transaction is imminent. When the market reaches a line, it will likely be forced to turn around, at least for a short time. Traders can trade this prediction and invest in a movement in the opposite direction of the previous movement. If you are using a high/low option, keep in mind that this is a short-term prediction and use expiration on the length of a period. You can also use the one-touch option. In this case, make sure to use a target price no more than half the distance to the next line.
- Trading the market breakout in the middle of the road. The midline is special because it can act as either resistance or support, depending on where the market is currently in relation to the line. When the market crosses the line, it changes its meaning. What a resistance now becomes a support, or vice versa. Traders can profit from this important event and invest in binary options in the direction of the breakout.
This simple way of making money is ideal for newbies. Experienced traders can also add another indicator to confirm predictions made by bollinger bands, for example a moving average.
3. Trade Average True Range (ATR)
Average True Range (ATR) is a perfect technical indicator for boundary options traders. Boundary options are a special type of binary options as they are the only one that does not require you to predict the direction of the market, which is perfect for traders who have difficulty predicting this type.
Boundary options define two target prices within equal distances from the current market price. One above the current market price, one below it. Your two selection wins; The market must trigger the target price before your selection ends. There is no need for it to stay at the price level, and it only has to touch a target price. A boundary option is a one-touch option with two target prices.
With boundary options, your task is not to predict which direction the market will move. Your task is to predict whether it will move far enough to reach either target price or not. ATR is the perfect indicator to make this prediction.
The ATR does one simple thing: it calculates the average range of past market periods. If the ATR has a value of 10 and you are viewing a chart with a 10-minute interval, for example, the asset has moved, on average, 10 points every 10 minutes.
You can adjust the amount of time you want the ATR to analyze. Most traders use a 14 period setting, which means that the ATR calculates the average range of the last 14 periods of your chart.
To trade ATR-based boundary options, you only have to compare the ATR reading with the target price.
Let’s go back to our previous example: in a 10-minute chart, the ATR has a value of 10. If your broker offers you an option with a target price 30 points away and expiration one Now, you know there’s a good chance that the market will hit one of the target prices. Your reasoning would look like this:
- The market has moved 10 points per period.
- To reach the target price in a straight move, the market would have to move 5 points per period. (Options have a 60 minute expiry and you are looking at a 10 minute chart. This means you have six periods until your option expires. Target price is 30 points. Divided by six periods, you will understand that the market will have to move an average of 5 points per period to get the market price in a straight line.)
- The average market movement per period is twice as high as the movement needed to reach the target price.
- Generally speaking, the market will never move in a straight line, but if it moves in the same direction for two consecutive periods, it is almost there. So there is a good chance that it will hit the target price.
As you can see from this example, you will always have to reduce the maximum price of the market. If the market moves in the same direction for 60 minutes, it will have a range of 60 points. This will never happen, which is why many traders use a bearish factor. For example, they multiply the maximum range by 0.5, and when the target price of the marginal option is closer to the result of this equation, they invest.
You can choose a discount factor according to your risk tolerance and experience. We recommend using a factor of 0.5 or less. The higher factors are too risky.
Also, consider the payout you receive for your selection. Some brokers offer high risk boundary option (far target price, higher payout) and low risk boundary option (close target price, lower payout). Higher payouts allow you to trade profitably when you win fewer trades, that’s why you can take more risk and use a higher discount factor.
Some traders also use the average directional movement (ADX) indicator. The ADX represents trend strength on a scale of 0 to 100. 0 indicates a complete lack of direction, 100 which all time periods are in the same direction. You can calculate your discount factor by dividing the value of ADX by 100.
- When the ADX reads 40, you use a discount factor of 0.4.
- When the ADX reads 70, you use a discount factor of 0.7.
With this strategy, you adapt your bearish factor to the current market environment.
Last word on technical indicators
Technical indicators and binary options are a great combination. Technical indicators allow you to make short-term predictions in any market; Binary options allow you to trade these predictions more profitably than other types of trading.
As with our examples of MFI/RSI, bollinger bands or ATR program, there is an indicator for any strategy. Find the right indicator for you, and you’re on your way to becoming a successful trader.
If you still need a broker with which you can trade binary options, check out our top list of the best brokers;